Arnaud Legout
10 mars 2011 de 11h à 12h : salle 25-26/101
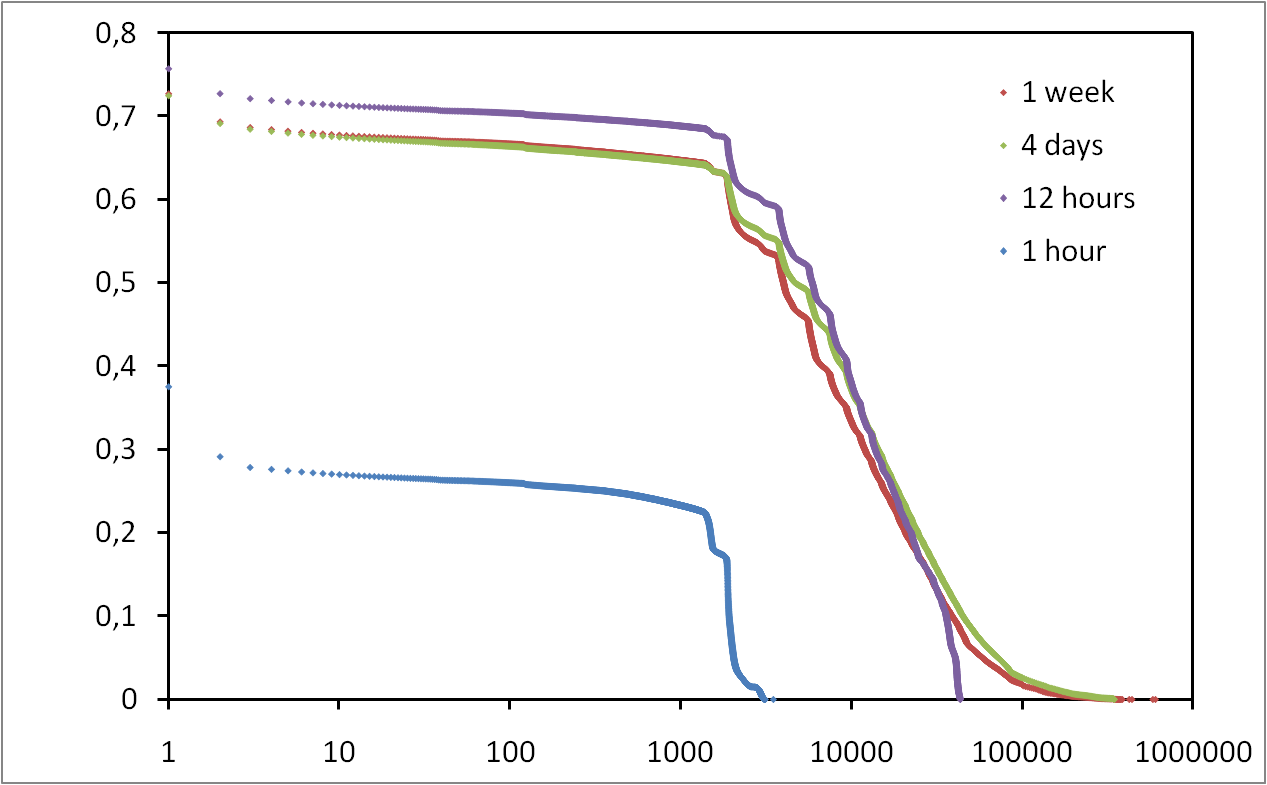
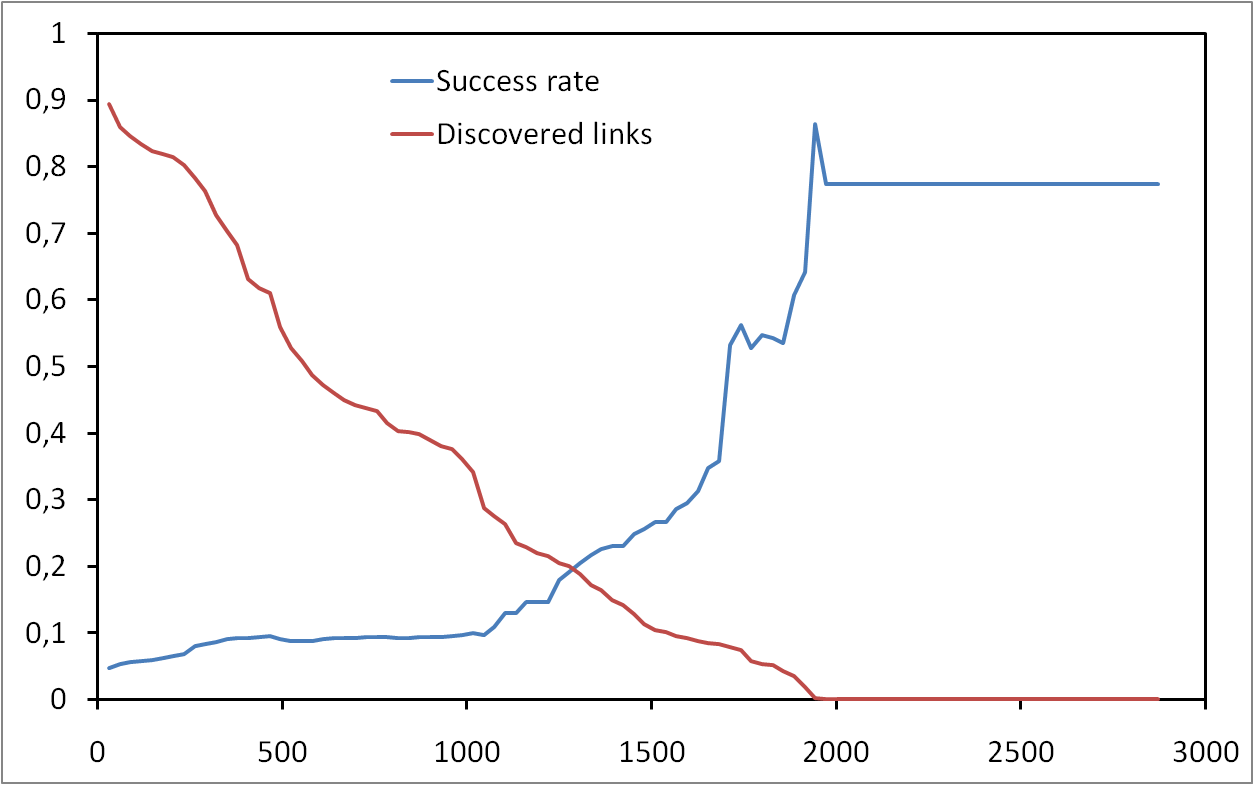
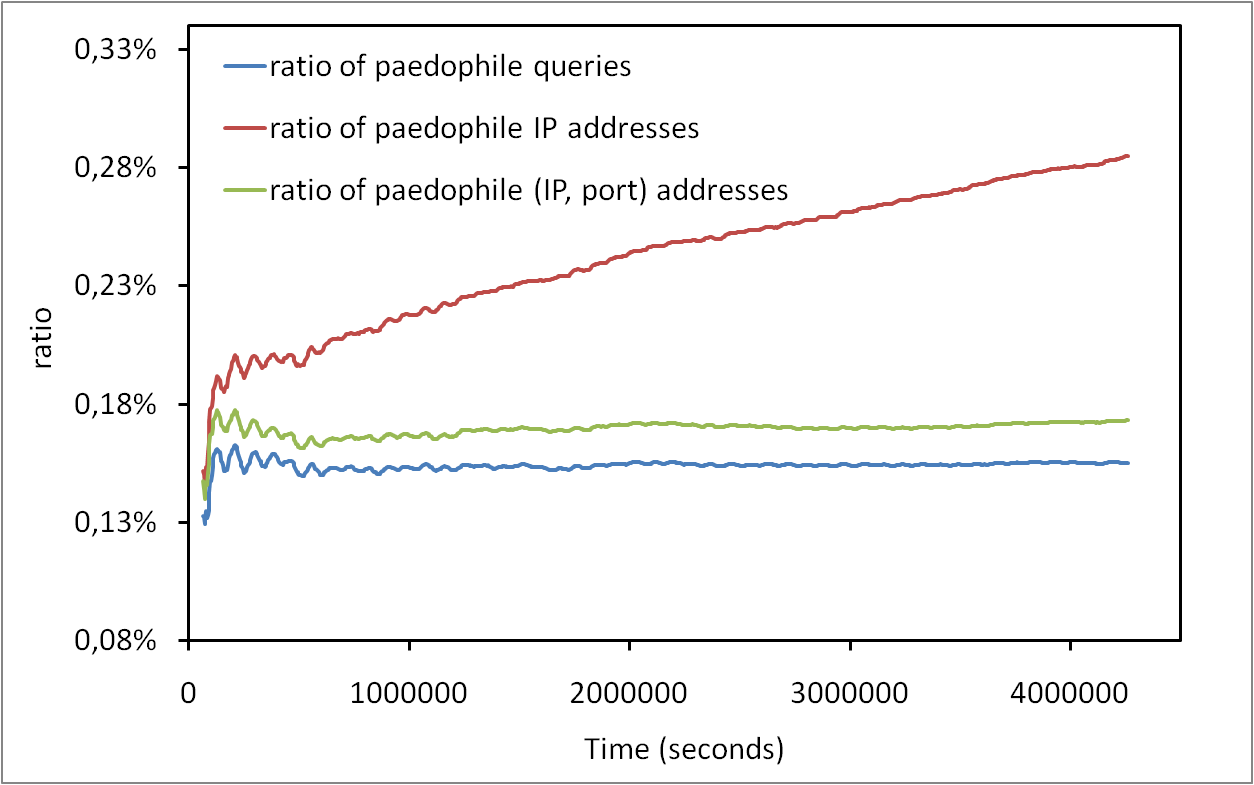
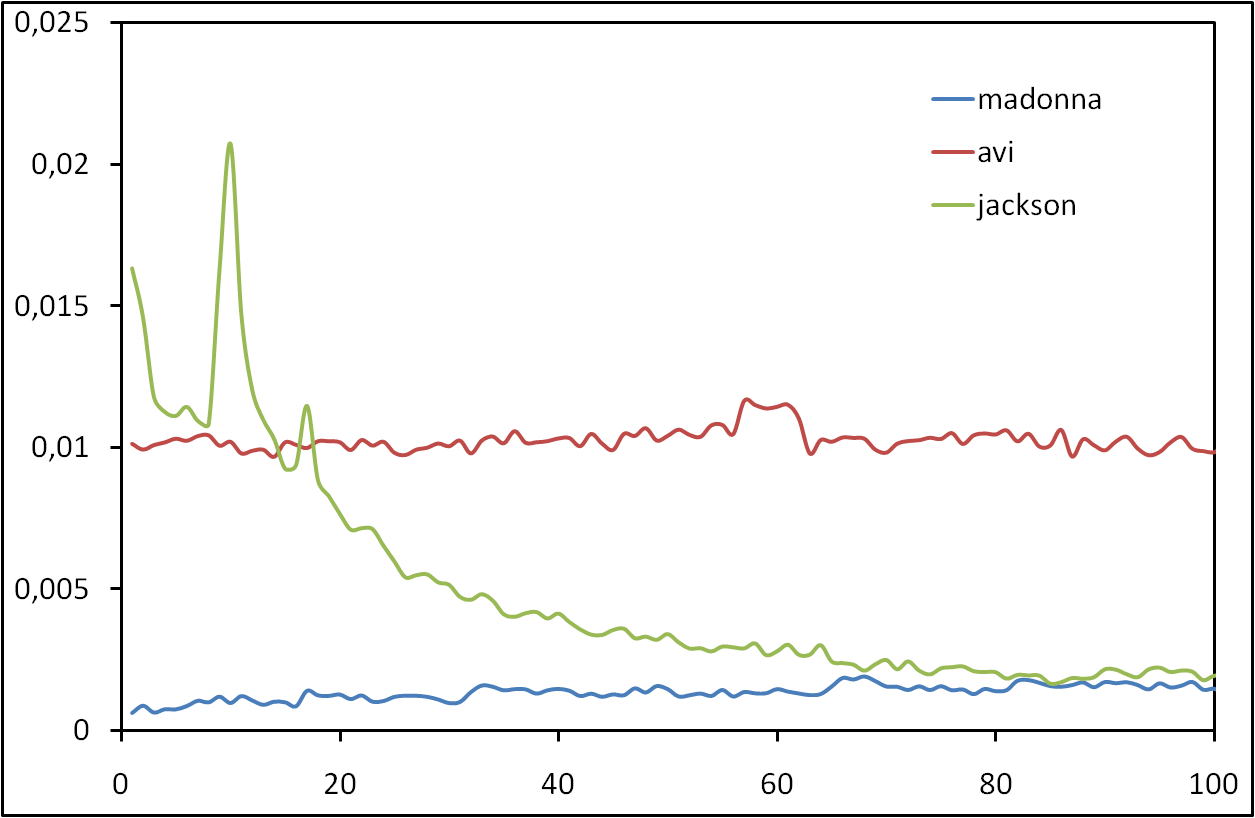
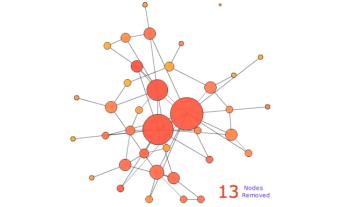
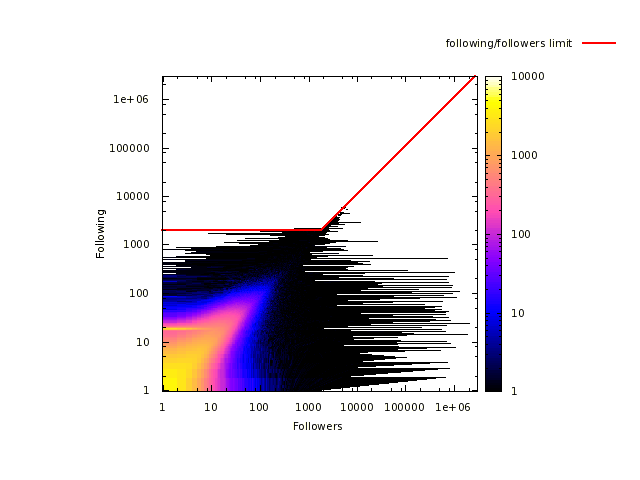
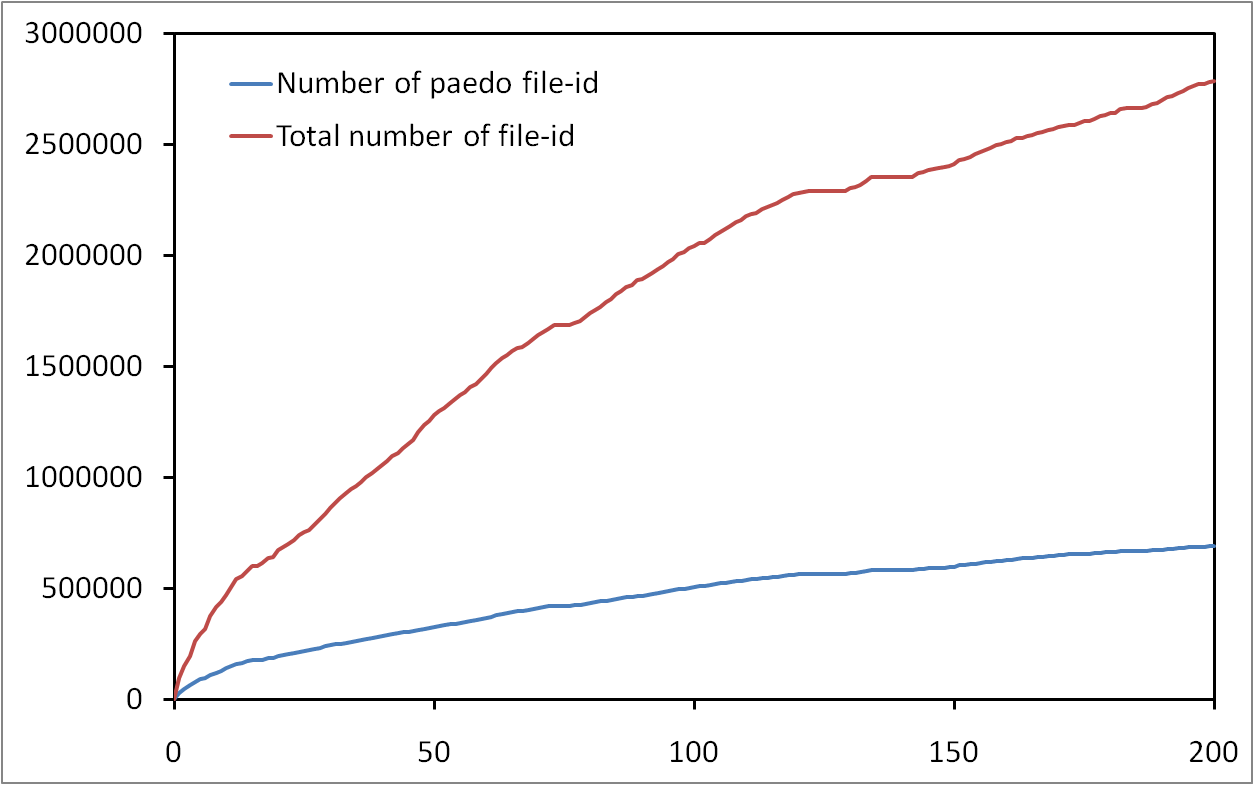
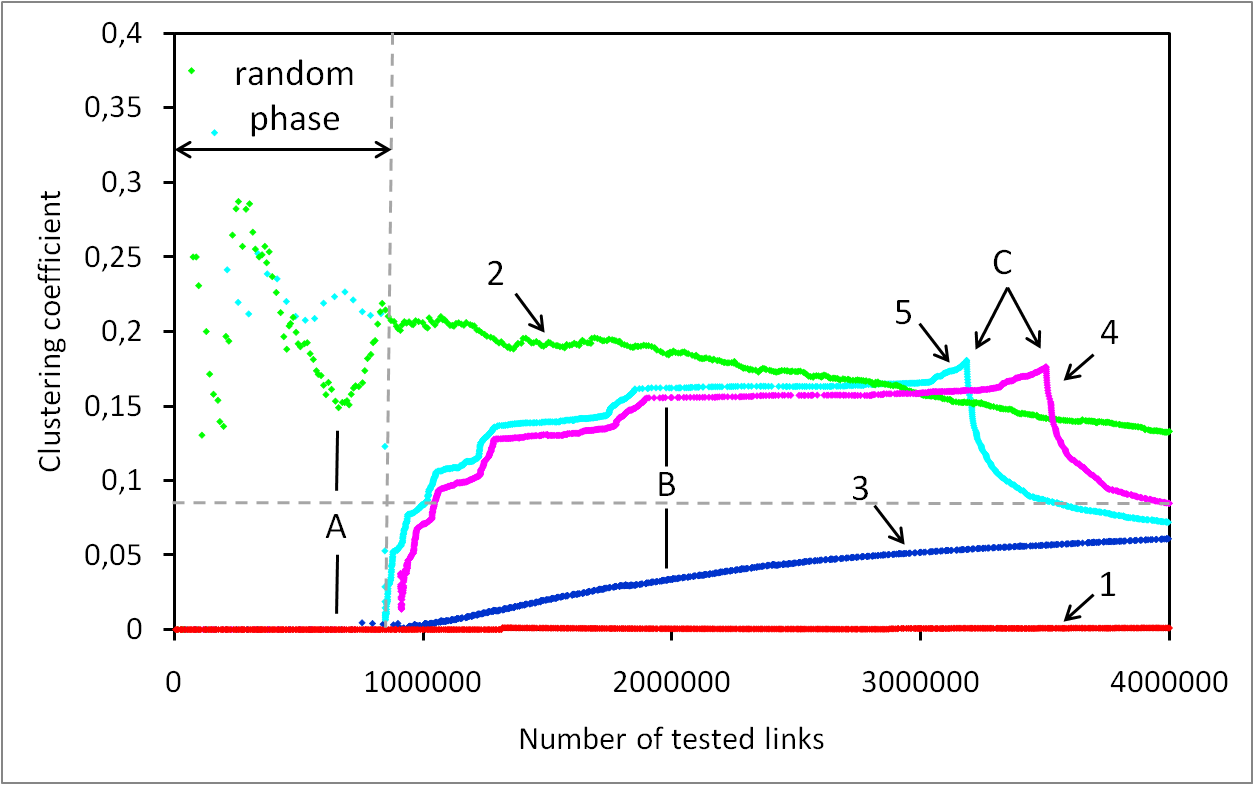
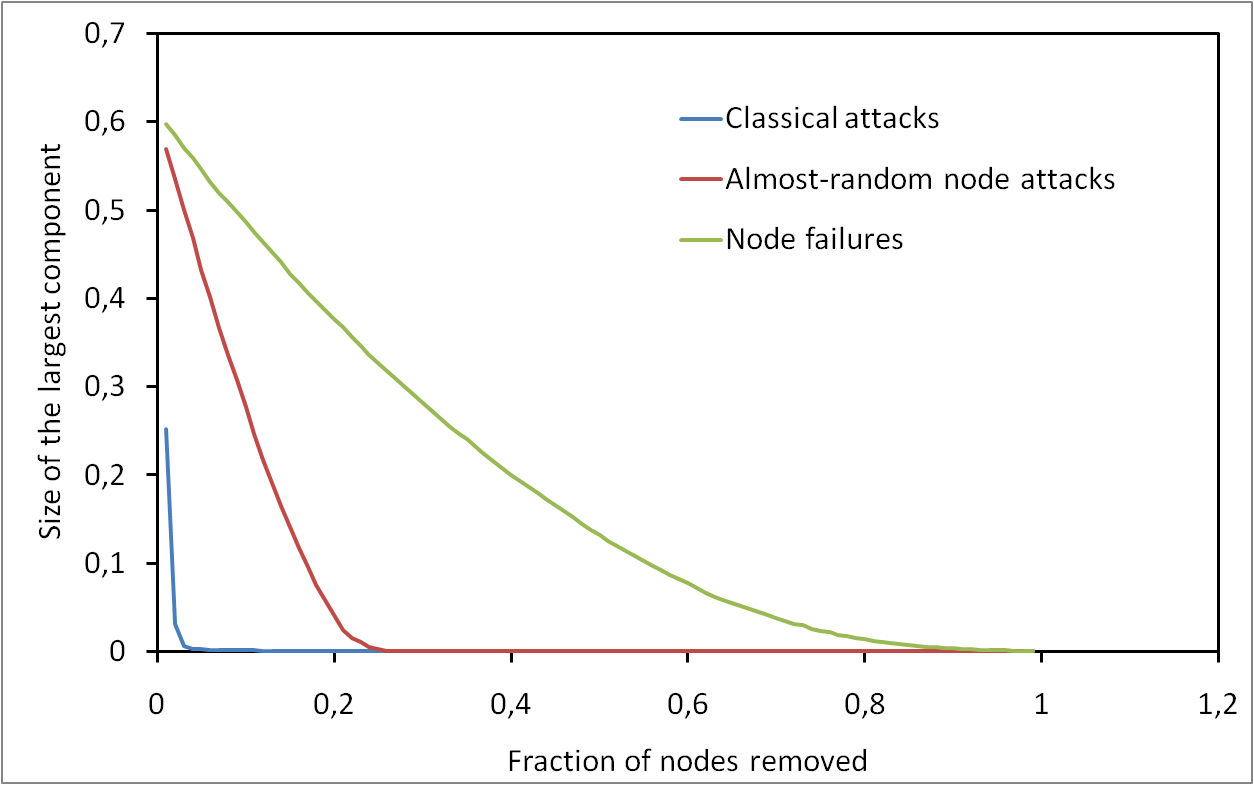
Les risques d’atteinte à la vie privée sur Internet sont largement sous estimés. Il est connu que les internautes laissent énormément d’informations personnelles sur, par exemple, les réseaux sociaux. Cependant, peu de gens savent que toute activité sur Internet laisse des traces. Dans cet exposé, nous allons montrer qu’il est possible de collecter ces traces à grande échelle et sans infrastructure dédiée. Plus précisément, nous allons montrer qu’il est possible de surveiller l’activité sur BitTorrent de centaines de millions d’internautes. Nous allons également montrer qu’en exploitant des mesures faites sur BitTorrent et sur un réseaux de voix sur IP, il est non seulement possible de lier à une identité réelle une liste de téléchargement de manière automatique, mais qu’il est également possible de suivre les déplacements d’un grand nombre de personnes sans que ces personnes n’aient aucun moyen de détecter ni de bloquer ces mesures.