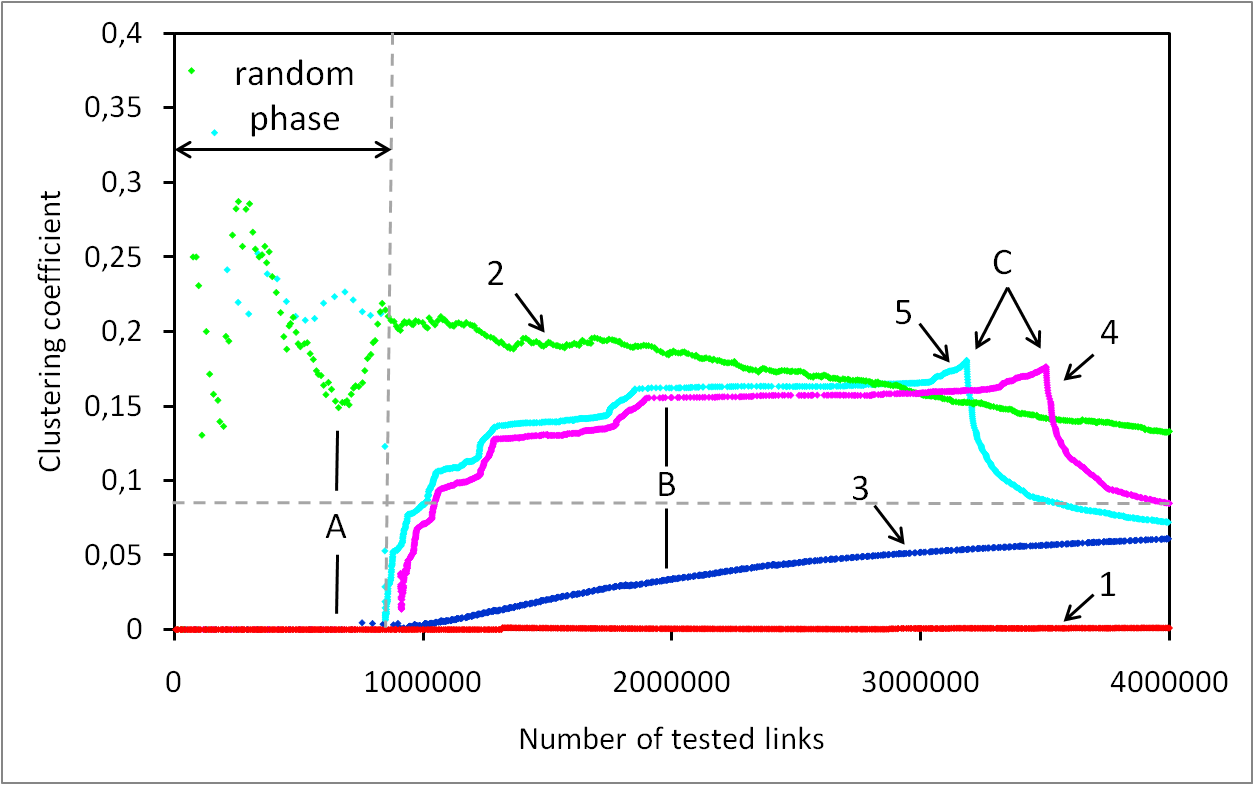
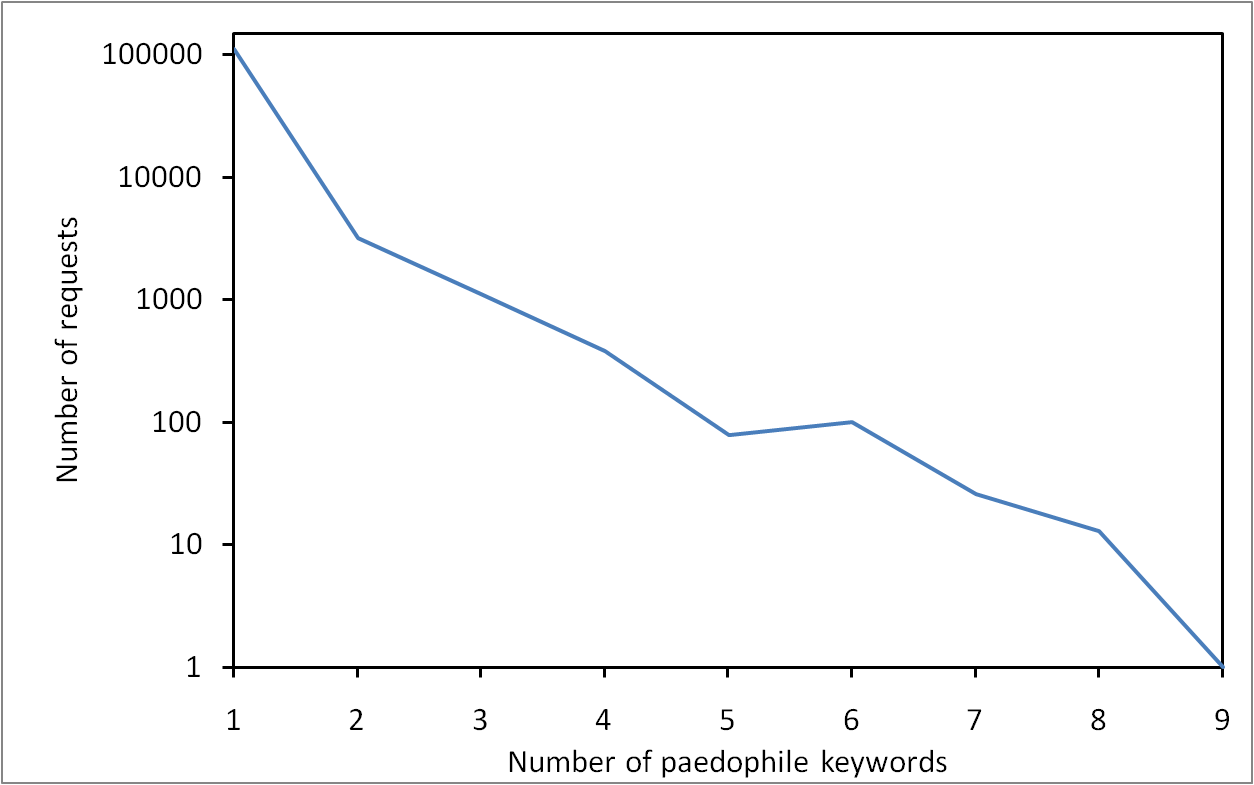
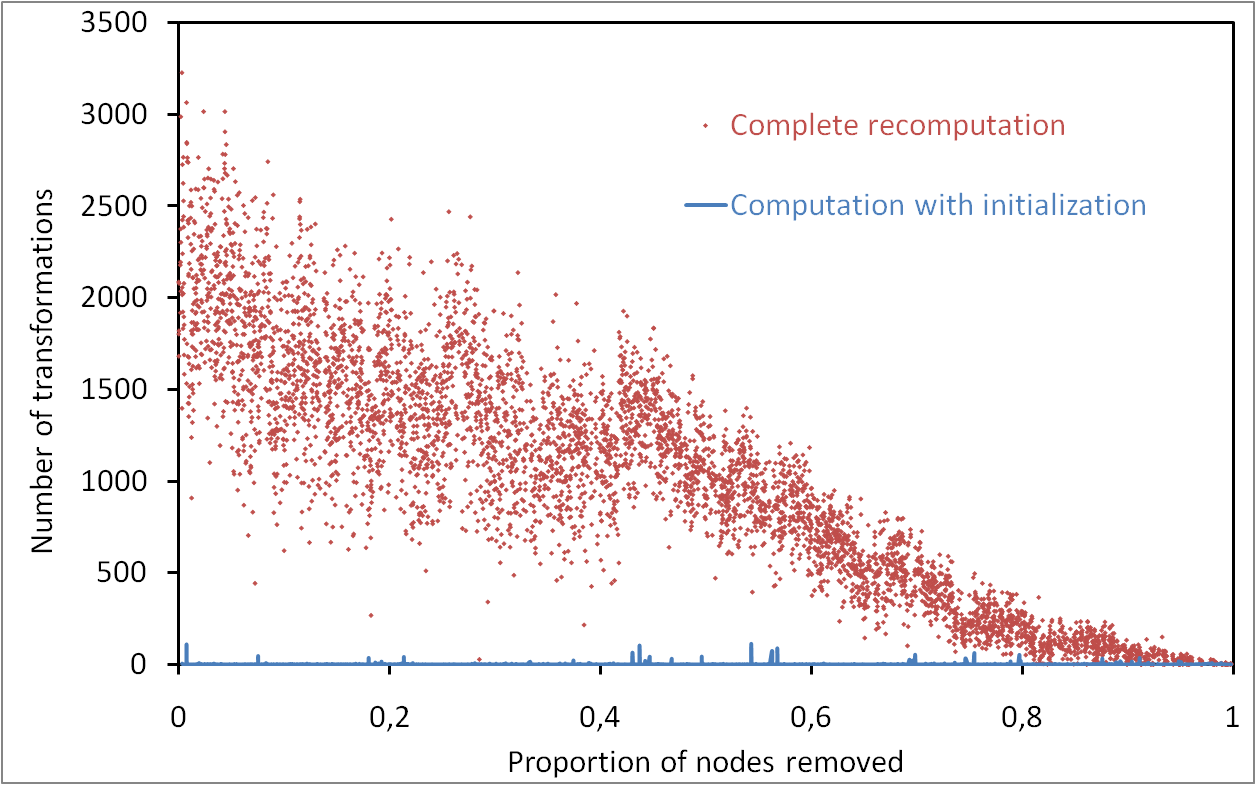
Measuring clustering coefficient with different strategies
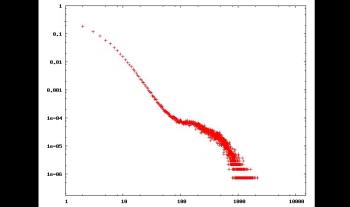
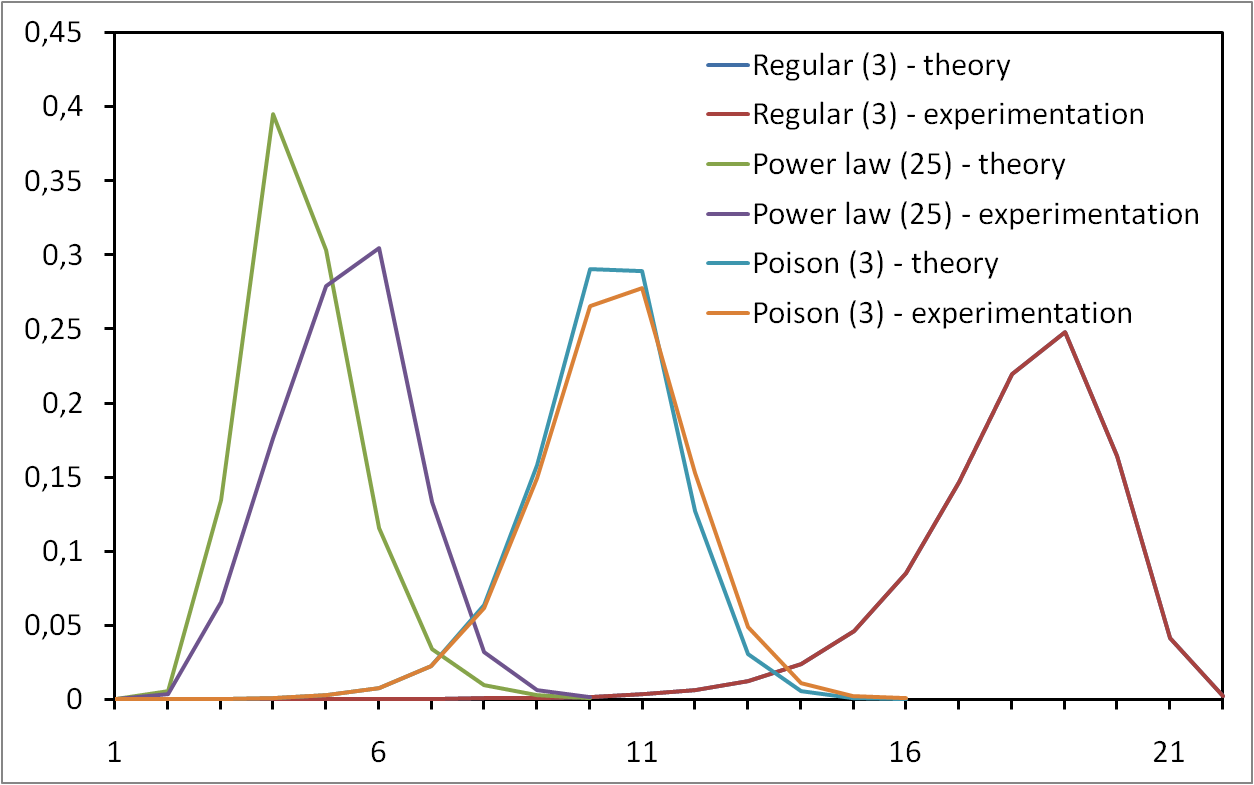
Evolution of degree distribution during measurement
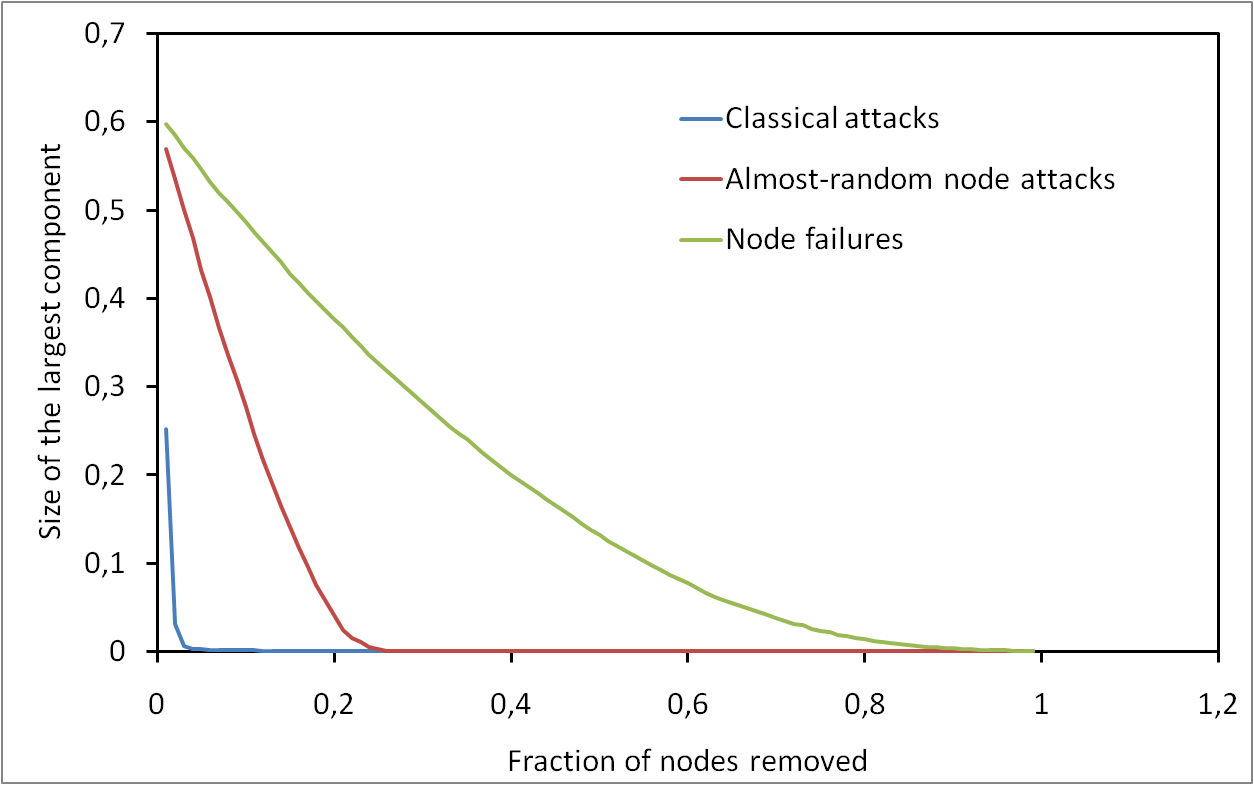
Network Robustness
Impact of Random Failures and Attacks on Poisson and Power-Law Random Networks
Clémence Magnien, Matthieu Latapy and Jean-Loup Guillaume
ACM Computing Surveys, 43 (3), 2011. Extended abstract published in LNCS, proceedings of the 8-th International Conference On Principles Of Distributed Systems OPODIS’04, 2004, Grenoble, France (title: Comparison of Failures and Attacks on Random and Scale-free Networks)
It appeared recently that the underlying degree distribution of a network may play a crucial role concerning its robustness. Empiric and analytic results have been obtained, based on asymptotic and mean-field approximations. Previous work insisted on the fact that power-law degree distributions induce a high resilience to random failure but a high sensitivity to some attack strategies, while Poisson degree distributions are quite sensitive in both cases. Then, much work has been done to extend these results. We focus here on these basic results, with the aim of deepening significantly our understanding of their origin and their limitations. We review in detail previous contributions and we give full proofs in a unified framework, in which the approximations on which these results rely are well identified. We then add to these known results a set of new ones aimed at enlightening some important aspects. We also provide extensive and rigorous experiments which make it possible to evaluate the relevance of the analytic results. We reach the conclusion that, even if it is clear that the basic results of the field are true and important, they are in practice much less striking than generally thought. The differences between random failures and attacks are not so huge and can be explained with simple facts. Likewise, the differences in the behaviors induced by power-law and Poisson distributions are not as striking as often claimed.
Mobile IPv6 Deployments: Graph-based Analysis and practical Guidelines
Guillaume Valadon, Clémence Magnien and Ryuji Wakikawa
Computer Communications, 32, 2009
The Mobile IPv6 protocol is a major solution to supply mobility services on the Internet. Many networking vendors have already implemented it in their operating systems and equipments. Moreover, it was recently selected to provide permanent IP addresses to end users of WiMAX and 3GPP2. Mobile IPv6 relies on a specific router called the home agent that hides location changes of the mobile nodes from the rest of the Internet. To do so, the mobile nodes’ traffic must flow through the home agent. This mandatory deviation produces longer paths and higher communication delays. In order to solve these problems, we describe a new approach to address deployments of Mobile IPv6 based on graph theory and could be applied to any operator’s network. In particular, we use notions of centrality in graphs to quantify increases of communication distances induced by dogleg routing and identify relevant home agents locations. We evaluate this approach using real-world network topologies and show that the obtained Mobile IPv6 performance could be close to direct paths ones. The proposed algorithm is generic and can be used to achieve efficient deployments of Mobile IPv6 as well as Home Agent Migration: a new Mobile IPv6 architecture using several distributed home agents.
Spreading of a file in a P2P system
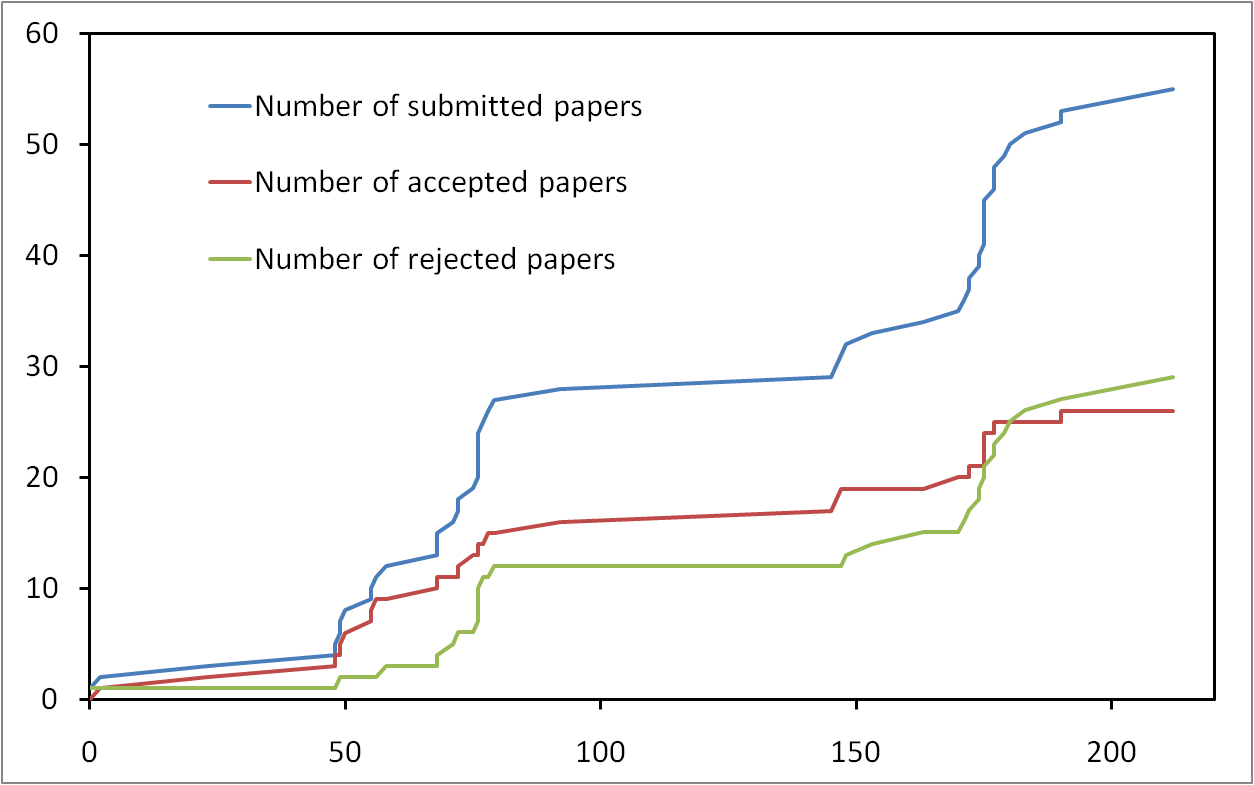
Impact of submission time on paper acceptation
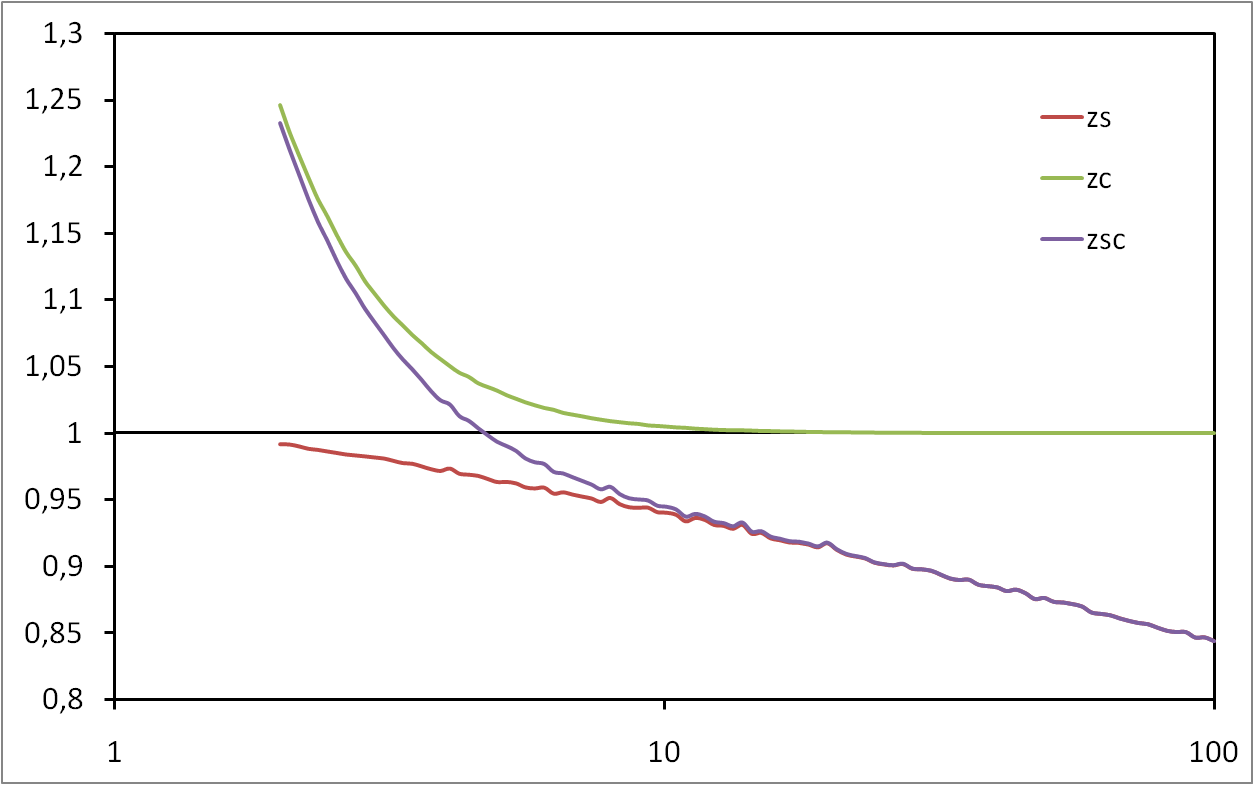
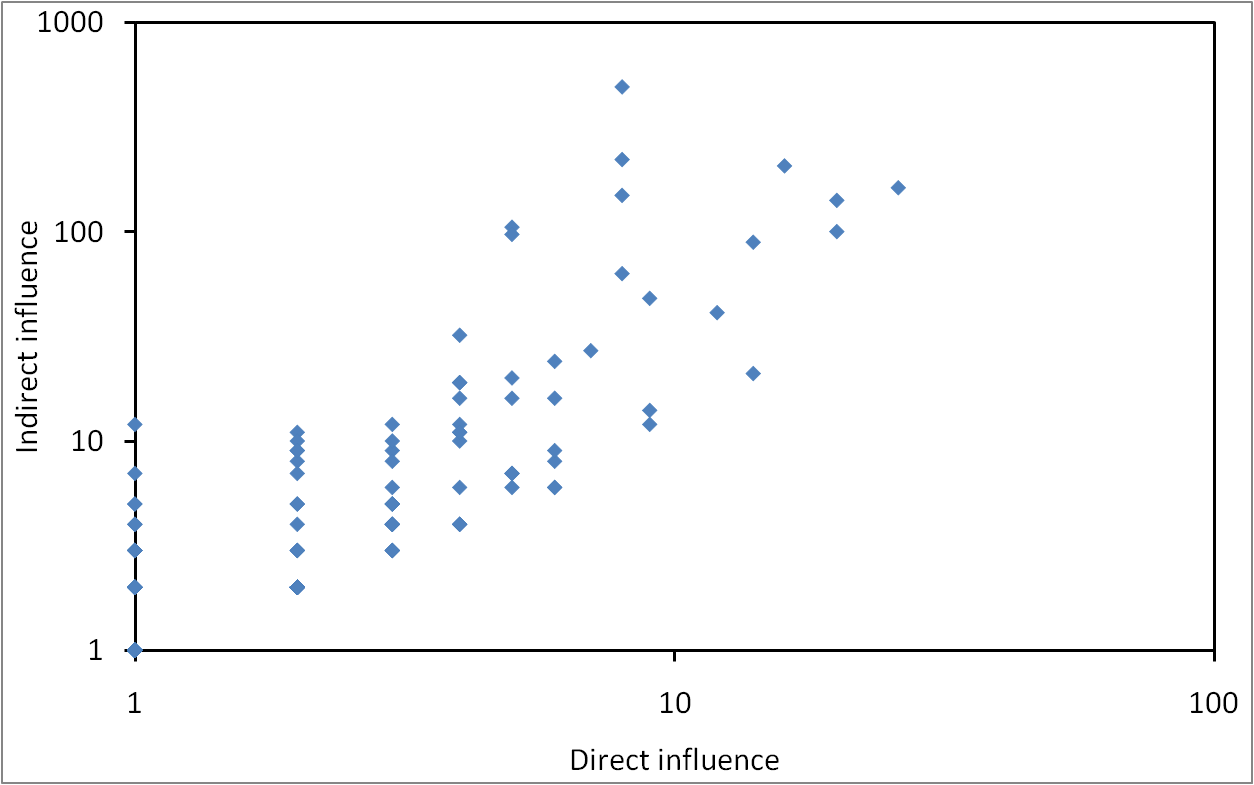
Bias in generated random graphs
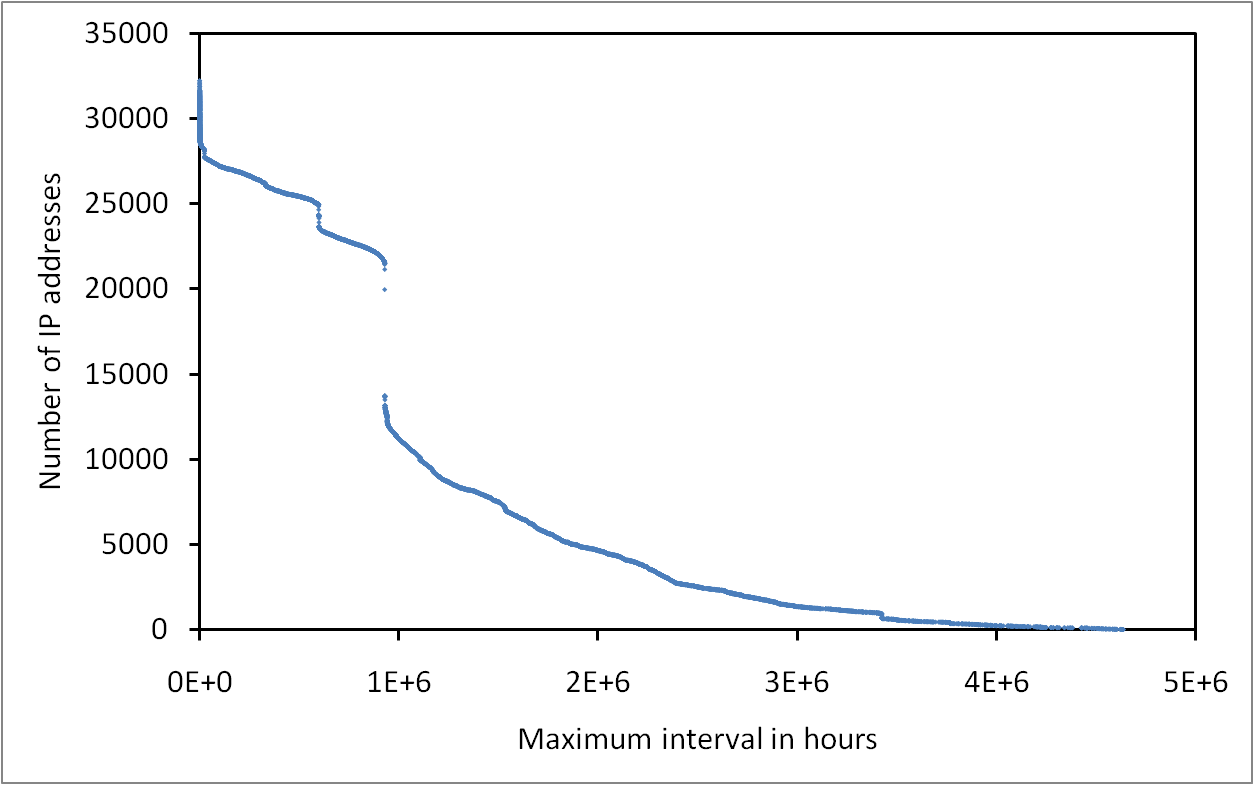
Interval between the discoveries of IP addresses from several monitors
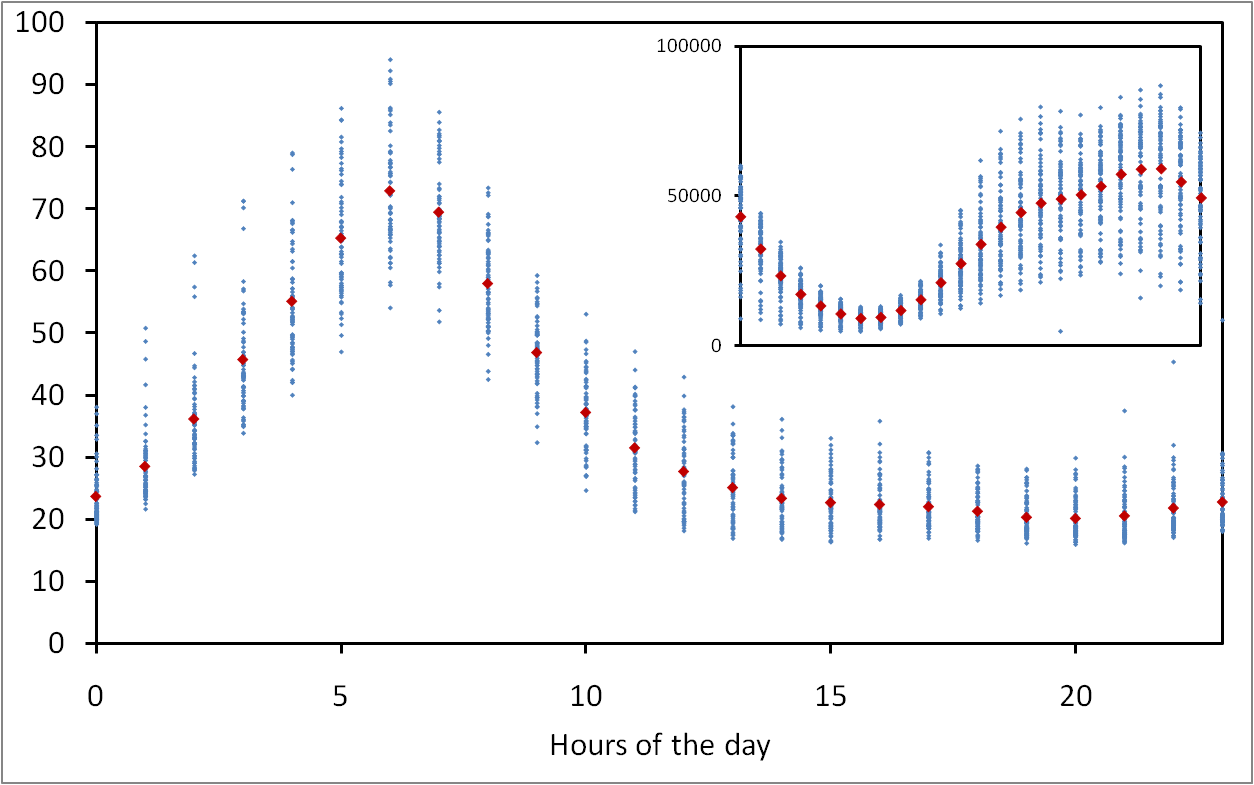
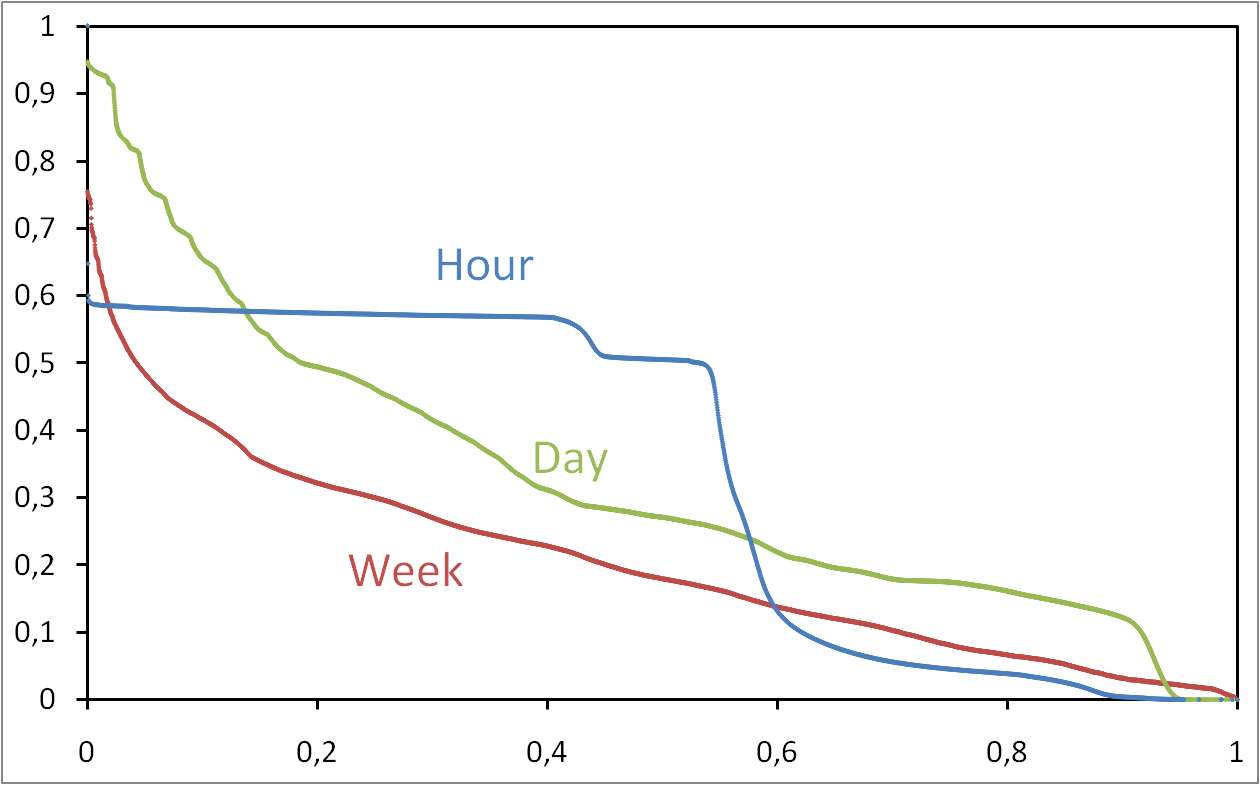
Typical days of search management for an eDonkey server
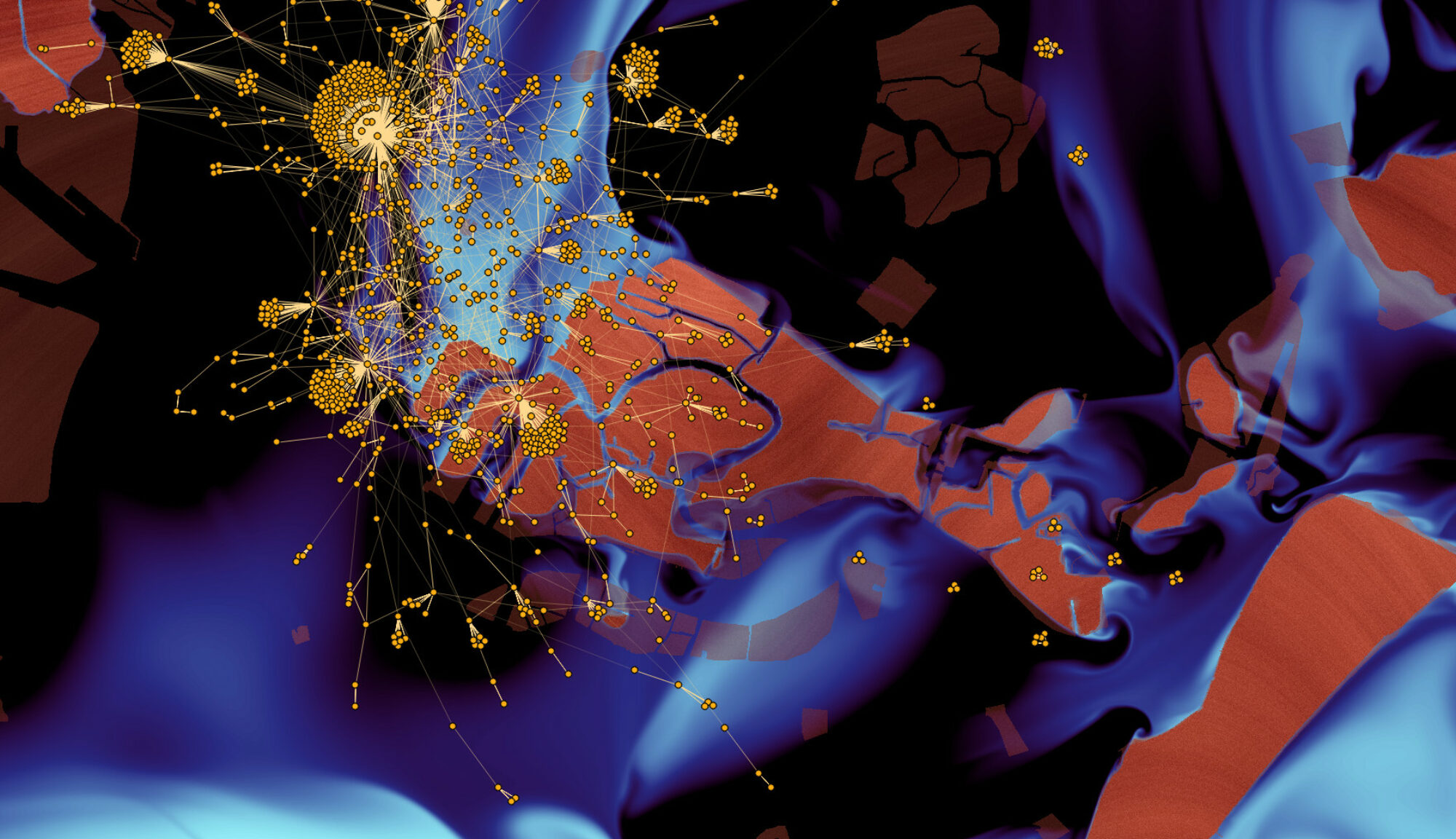
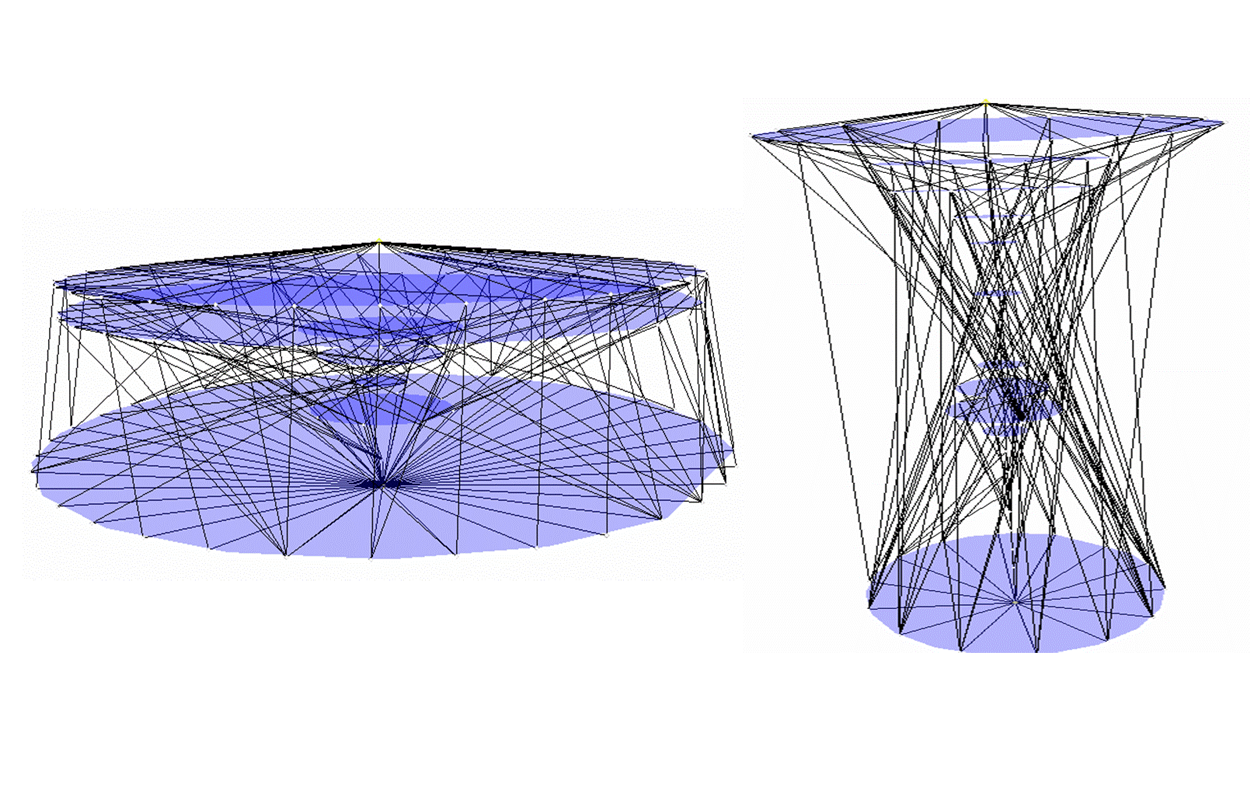
Efficient Measurement of Complex Networks Using Link Queries
Fabien Tarissan, Matthieu Latapy and Christophe Prieur
In Proceedings of the IEEE International Workshop on Network Science For Communication Networks (NetSciCom’09)
Complex networks are at the core of an intense research activity. However, in most cases, intricate and costly measurement procedures are needed to explore their structure. In some cases, these measurements rely on link queries: given two nodes, it is possible to test the existence of a link between them. These tests may be costly, and thus minimizing their number while maximizing the number of discovered links is a key issue. This is a challenging task, though, as initially no information is known on the network. This paper studies this problem: we observe that properties classically observed on real-world complex networks give hints for their efficient measurement; we derive simple principles and several measurement strategies based on this, and experimentally evaluate their efficiency on real-world cases. In order to do so, we introduce methods to evaluate the efficiency of strategies. We also explore the bias that different measurement strategies may induce.
Ten weeks in the life of an eDonkey server
Frédéric Aidouni, Matthieu Latapy and Clémence Magnien
Sixth International Workshop on Hot Topics in Peer-to-Peer Systems (Hot-P2P 2009), May 29, 2009, Rome, Italy
This paper presents a capture of the queries managed by an eDonkey server during almost 10 weeks, leading to the observation of almost 9 billion messages involving almost 90 million users and more than 275 million distinct files. Acquisition and management of such data raises several challenges, which we discuss as well as the solutions we developed. We obtain a very rich dataset, orders of magnitude larger than previously avalaible ones, which we provide for public use. We finally present basic analysis of the obtained data, which already gives evidence of non-trivial features.